Scalingo Database Addons
You applications need databases to store your data. As we believe your data should be located geographically close to your application servers we support the most common types of database.
We ensure your database is located at the same location as your applications. It provides the best performances and latency possible. Moreover you know where your data is.
Database Plans
Scalingo offers three classes of service with distinct characteristics, enabling you to choose the level of performance, replication, security and price that suits your use case. All our plans are 100% managed and billed on demand.
You can seamlessly switch between plans and service classes in just a few seconds, from the smallest single-node instance plan to the largest multi-node cluster plan, and everything in between.
Sandbox
The Sandbox class is designed for testing and development environments. It is ideal for evaluating our service or testing new technology.
It is not suitable for hosting production workloads due to its performance limitations and lack of guaranteed availability and backups.
Starter
The Starter class is designed for applications under development and non-critical, production environments. With an SLA of 98% and back-up retention of one month, it offers a secure, high-performance environment for a wide range of use cases.
Business
The Business class is Scalingo’s flagship. It guarantees high availability and reliability, which are essential for critical production applications. Thanks to hot replication of your data on a standby instance, we ensure service continuity along with a 99.96% SLA. For complete protection, backup retention is extended to 1 year.
Database Types
SQL
NoSQL
Encryption at Rest
All databases created after the 6th of January 2019 have encryption at rest enabled. In other words, all your data is encrypted before being stored on disk.
Encryption at rest leverages a feature of the Linux Kernel allowing to encrypt
data at the disk level named dm-crypt. The algorithm used is
aes-xts-plain64 with a key size of 256 bits and hashed using SHA-256. This
method is considered secure and standard in the industry. To reduce the attack
surface, each instance of each database has its own cryptographic key to
protect its data, so getting access to one key wouldn’t allow an attacker to
get plain data from another database. The keys are stored in a database which
is itself encrypted and protected by authentication.
Communication With TLS
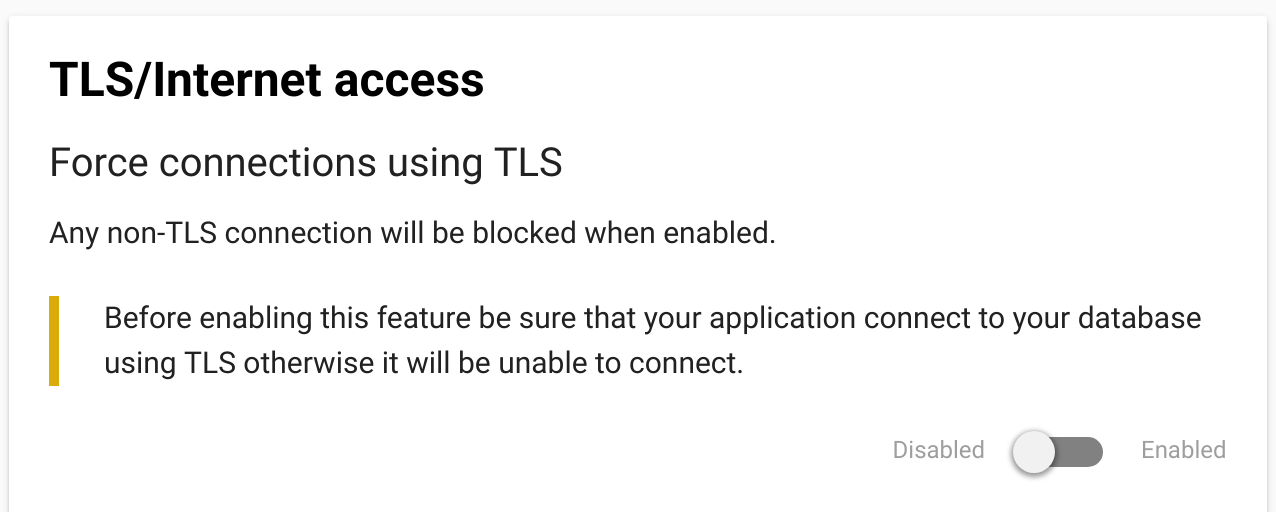
We enable for all database types the possibility to connect to them using TLS. By default, you can connect both with or without TLS to your database. You can also enforce all connections to use TLS by activating the “Force TLS Connections” feature in the web dashboard of your addon:
Moreover, we also encrypt all communications between the members of cluster:
- from the gateways to the leader,
- from the leader to the followers,
- between the cluster orchestrator and its database for PostgreSQL databases.
Connection Timeouts
Most of our high availability setups contain a HAProxy as entry point to the actual database nodes. This HAProxy has a few timeouts configured which may impact your application, especially if you reuse connections. The concerned databases are:
- Scalingo for Elasticsearch®:
- Timeout when the client is inactive: 1 minute.
- Timeout when the server is inactive: 2 minutes.
- Maximum allowed time to wait for a complete HTTP request: 5 seconds.
- Scalingo for PostgreSQL®:
- Timeout when the client is inactive: 1 day.
- Timeout when the server is inactive: 30 minutes.
- Inactivity timeout on the client side for half-closed connections: 5 minutes.
- Scalingo for Redis®:
- Timeout when the client is inactive: 5 minutes.
- Timeout when the server is inactive: 5 minutes.
- Inactivity timeout on the client side for half-closed connections: 1 hour.